- Community
- RUCKUS Technologies
- RUCKUS Lennar Support
- Community Services
- RTF
- RTF Community
- Australia and New Zealand – English
- Brazil – Português
- China – 简体中文
- France – Français
- Germany – Deutsch
- Hong Kong – 繁體中文
- India – English
- Indonesia – bahasa Indonesia
- Italy – Italiano
- Japan – 日本語
- Korea – 한국어
- Latin America – Español (Latinoamérica)
- Middle East & Africa – English
- Netherlands – Nederlands
- Nordics – English
- North America – English
- Poland – polski
- Russia – Русский
- Singapore, Malaysia, and Philippines – English
- Spain – Español
- Taiwan – 繁體中文
- Thailand – ไทย
- Turkey – Türkçe
- United Kingdom – English
- Vietnam – Tiếng Việt
- EOL Products
- RUCKUS Forums
- RUCKUS Technologies
- RUCKUS Self-Help
- How to troubleshoot DNS with help of wireshark
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
How to troubleshoot DNS with help of wireshark
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
10-24-2023 02:11 AM - edited 11-03-2023 09:18 AM
DNS is a directory of domain names that align with IP, and it bridges the gap between computer and human language.
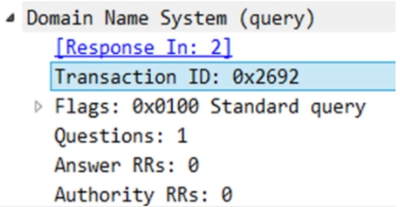
There are basically two packets when we observe DNS in Wireshark - query and response packet as show in the screenshot:
>The transaction id is same in both query and response.
Flags:
A>If the first bit in DNS flag is zero that means it’s a DNS query packet.
B >If it's 1 then it’s a response packet
>Opcode number are of four different values signifies whether it’s an update packet or not for example:
If the value of the opcode subfield is 0 then it is a standard query.
The value 1 corresponds to an inverse of query that implies finding the domain name from the IP Address.
The value 2 refers to the server status request.
The value 3 specifies the status reserved and therefore not used.
>Truncated field tells us whether packet it is cut shot or not.
>Recursion means where one DNS server communicates with several other DNS server to hunt down an ip address and return it to the client
>Questions field signifies whether you have queried for something or not. Default is 1 for any request sent or received.
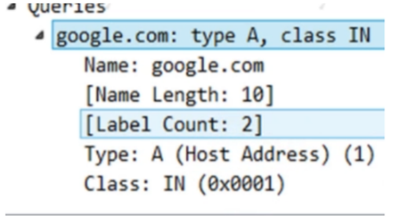
>Queries signifies what is the host address of google.com and IN stands for internet class.
>Time column is only available in query response field, it tells how long response took to comeback.
>Reply code all 0 means it’s a positive response no error.
>Reply code 2 means server failure.
>Rely code 3 req name is not in server.
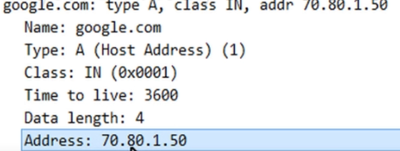
>Answer section tell host address of google.com is 70.80.1.50 this is positive response.
>A positive response will have answer section here.
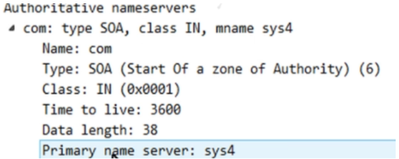
>DNS authoritative response: It tell client that whatever record resource you have asked the server is not available as shown in the above screen shot. If it is available, then it sends positive response.
- Labels:
-
ICX
-
RUCKUS Self-Help
-
AAA
2 -
Access points
48 -
Analytics
3 -
AP Certificate error
1 -
AP Controller Connectivity
5 -
AP Management
8 -
AP migration
1 -
AP reporting
1 -
API
2 -
Authentication Server
2 -
Client Management
1 -
Cloud
20 -
Cloud ICX
1 -
Cloudpath
23 -
Cluster synchronization
1 -
Deployment
2 -
Firmware Recommendation
1 -
Firmware Upgrade
5 -
Guest Access
2 -
ICX
73 -
ICX Switch Management
7 -
Installation
5 -
IoT
1 -
Licensing
1 -
Mobile Apps
2 -
Monitoring
1 -
Poe
2 -
RADIUS
2 -
Ruckus Cloud
1 -
RUCKUS Self-Help
209 -
Security
6 -
SmartZone or vSZ
64 -
Stacking
1 -
SZ ICX Connectivity
1 -
Traffic Management-
1 -
UMM
3 -
Unleashed
15 -
User Management
1 -
Venue Management
1 -
Wired Throughput
2 -
Wireless Throughput
1 -
WLAN Management
5 -
ZoneDirector
15
- « Previous
- Next »